Liver
The liver is a gland extramural anficrina (endocrine and exocrine secretion) located below the diaphragm and located between it and the transverse colon and stomach. It is the largest organ in the human body after the skin. It plays a key role in metabolism and has a number of processes, including the storage of glycogen, the synthesis of proteins in the plasma, removing toxic substances from the blood. It produces bile, which is important in the processes of digestion and is up to the 6th month of intrauterine life the most important organ hemopoietic. In the case of splenectomy, liver function can be summarized hematopoietic compensating for the lack of the spleen.
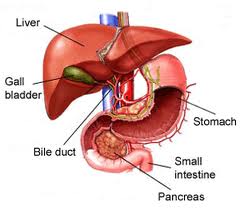
The medical terms related to the liver often use the word "liver" or the prefix "hepatorenal" named in the Greek language of the liver, hepar, hepatis; his name in Italian derives from the Latin iecur ficatum (liver with figs), a recipe in vogue in ancient Rome, which consisted in fattening, feeling or bake the foie gras with figs.
Alerts: If you want to know more fresh update helpful articles enter your email address below and be notified by mail.








